Low Bed Trailer Comprehensive Guide:What is a Lowboy/Lowbed Trailer?
Are you interested in learning more about trailers that can handle exceptionally heavy loads? The lowbed trailer (also known as a lowboy trailer) may be just what you're looking for, with its impressive capacity to transport up to 150 tons.In this guide, we will provide comprehensive information about lowbed trailers and how to choose the best one for your business needs. With the insights offered, you will be well-equipped to make a cost-effective purchase of a lowboy/lowbed trailer from China.
By considering this information, you can make an informed decision about the ideal lowbed trailer tailored to the specific requirements of your business.
What is Low Bed Trailer?
A low bed trailer, also known as a lowboy trailer, is a specialized type of trailer designed for transporting oversized, heavy, or tall cargo. With a lower deck height compared to traditional flatbed trailers, low bed trailers offer increased clearance to accommodate tall loads while adhering to road and bridge height restrictions.
Low bed trailers are commonly used across various industries, including construction, mining, energy, and agriculture. They are designed to transport heavy machinery and equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, cranes, tractors, and other large items that can't be easily transported by standard trailers.
These trailers come in several configurations, with features like multiple axles to distribute weight evenly and provide additional support. Some low bed trailers are also equipped with detachable goosenecks, which allow the front of the trailer to be lowered to the ground, simplifying the process of loading and unloading heavy or oversized equipment.
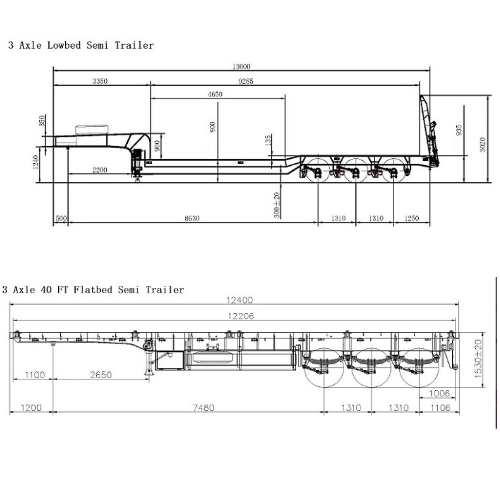
Lowbed trailers come in various capacities, ranging from 20 tons, 30 tons, 50 tons, 70 tons, 80 tons, and 100 tons, to 120 tons and even 150 tons. Depending on their capacity, they utilize different numbers of axles, from 2, 3, or 4 axles, extending up to 7 or 8 axles.
By offering greater height clearance, stability, and load capacity, low bed trailers play an essential role in the transportation of heavy and oversized cargo for various industries, enabling efficient and safe transportation.
Types of Low Bed Trailers
Low bed trailers, also known as lowboy trailers, are used to transport large and heavy equipment, machinery, and vehicles. They have a low deck height that provides enhanced stability and allows for the transport of taller loads. There are various types of low bed trailers to accommodate different types of cargo:
Single-drop low bed trailer: This type features one drop in the deck, usually just behind the gooseneck. It provides a lower deck height for taller loads and offers moderate hauling capacity.
Double-drop low bed trailer: The double-drop has two drops in the deck offering a lower central deck height. It allows for the transportation of heavier and taller equipment that might not fit on a single-drop low bed trailer.
Extendable low bed trailer: An extendable low bed trailer can be extended to accommodate larger and longer cargo. It offers flexibility in hauling oversized or specialized loads that do not fit on standard low bed trailers.
RGN (Removable Gooseneck) low bed trailer: The RGN trailer features a detachable gooseneck, allowing the front of the trailer to be lowered onto the ground for loading large equipment. It provides easier access for loading and unloading heavy machinery.
Step deck (drop deck) trailer: A step deck trailer features two deck levels, with the upper deck being shorter and the lower deck being longer. It is suitable for transporting freight with height restrictions, but doesn't offer as low a deck height as other low bed trailers.
Hydraulic low bed trailer: These trailers come with hydraulic systems that allow the cargo platform height to be adjusted as needed. They are ideal for transporting heavy machinery, equipment, or vehicles that require a stable and flexible hauling solution.
Fixed-neck low bed trailer: These low bed trailers have a fixed neck that does not detach from the main deck. They necessitate the use of a loading ramp for cargo loading and unloading. They are often more cost-effective than RGN trailers but offer less flexibility.
Structures of Low Bed Trailers
Low bed trailers are designed with specific features to facilitate the safe and efficient transportation of heavy machinery, equipment, or vehicles. The structure of low bed trailers can be categorized into several key components:
Gooseneck: This is the connection point between the trailer and the towing vehicle. Goosenecks come in different forms; fixed, removable, or folding. Removable goosenecks (RGNs) allow the front of the trailer to be lowered onto the ground, creating a ramp for loading and unloading cargo.
Deck: The deck is the main platform where cargo is placed and secured. Low bed trailers typically have a drop deck or double-drop deck design. These configurations offer a lower center of gravity, increased stability, and the ability to carry taller loads.
Axles: Low bed trailers typically have multiple axles to distribute the weight of heavy loads and improve stability. The number of axles depends on the trailer configuration and the weight capacity of the trailer. Trailers can be equipped with 2, 3, 4, or even more axles to handle a wide range of payloads.
Suspension System: The suspension system is critical for maintaining stability and absorbing shock during transportation. Common suspension types include air suspension, mechanical leaf spring suspension, and hydraulic suspension. The choice of suspension system depends on the specific requirements of the cargo and road conditions.
Wheels and Tires: Robust wheel and tire configurations ensure smooth transportation of heavy loads across various road conditions. Low bed trailers typically have heavy-duty tires designed to handle high payloads.
Braking System: A reliable and efficient braking system is crucial for the safe transportation of heavy and large loads. Most low bed trailers come with air brakes or ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) for enhanced safety and control.
Outriggers: Outriggers are optional components that extend from the sides of the trailer to provide additional support and stability for wide cargo loads.
Ramps and Loading System: Depending on the type of low bed trailer, loading and unloading systems can vary. Trailers can use fixed ramps, adjustable hydraulic ramps, or removable goosenecks to facilitate the loading and unloading process.
Applications of Low Bed Trailers
Low bed trailers are versatile and widely employed in various industries for transporting heavy, oversized, or specialized loads. Some common applications of low bed trailers include:
Construction Industry: They are used to transport heavy construction equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, cranes, and wheel loaders, between job sites or from manufacturers to project sites.
Oil and Gas Industry: Low bed trailers are employed to haul drilling equipment, large pipes, pressure vessels, and other heavy machinery in oil and gas exploration, extraction, and refining operations.
Mining Industry: These trailers facilitate the transportation of large mining equipment, such as dump trucks, heavy drilling machines, and earthmovers, to and from mining sites.
Wind Energy: Low bed trailers are used to transport wind turbine components, such as tower sections, nacelles, and blades, to wind farm locations.
Transportation of Heavy Vehicles: The low deck height and large payload capacity make low bed trailers ideal for transporting trucks, buses, military vehicles, and other heavy or oversized vehicles.
Agricultural Industry: They are used to transport large agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, to and from farms or between agricultural sites.
Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment: Low bed trailers can be utilized to move heavy machinery, boilers, transformer units, and other industrial equipment used in manufacturing and production facilities.
Railroad Industry: They are employed to transport railcars, locomotives, and other railroad equipment, facilitating maintenance and construction of railway networks.
Infrastructure Projects: Low bed trailers assist in moving oversized components, such as bridge sections, large concrete beams, and precast tunnel segments, required for large infrastructure projects like highways, bridges, and tunnels.
Shipbuilding and Maritime Industry: They enable the transportation of large or heavy ship components and maritime equipment to shipyards and ports.
Advantages of Low Bed Trailers
Low bed trailers offer several advantages that make them an essential choice for transporting heavy, tall, or oversized cargo. Some of these advantages include:
Increased Load Capacity: Low bed trailers have a lower deck height that allows for a higher legal payload by providing additional clearance. This enables the transportation of taller, heavier loads with ease.
Greater Stability: The low deck height ensures a lower center of gravity, which improves stability during transportation, minimizing the risk of accidents or damage to the cargo.
Versatility: Low bed trailers can accommodate a wide range of cargo types and sizes, making them suitable for various industries like construction, mining, oil and gas, agriculture, and more.
Easy Loading and Unloading: Depending on the type of low bed trailer, loading and unloading can be simplified through the use of ramps, removable goosenecks, or hydraulic systems. This allows for efficient and safe handling of heavy machinery and equipment.
Flexible Configurations: Low bed trailers come in multiple configurations, such as single-drop, double-drop, extendable, RGN, and more, allowing for customization to meet specific transportation requirements.
Improved Safety: The low center of gravity and robust suspension system enhance the overall safety and control while on the road, reducing the risk of rollovers or cargo shifting.
Wide Load Accommodation: With the help of outriggers, low bed trailers can adjust to accommodate wide or oversized loads, ensuring secure transportation.
Reduced Transportation Costs: Low bed trailers can often transport heavy machinery or equipment without the need for additional escort vehicles, specialized permits, or route planning, which can result in reduced transportation costs.
Low Bed Trailers load capacity calculation
To calculate the load capacity of a low bed trailer, you need to consider several key factors, including the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR), the payload capacity, and other factors. Here's a step-by-step guide to calculating a low bed trailer's load capacity:
Determine GVWR: The Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) of a low bed trailer is the maximum weight the trailer can carry, including its empty weight (tare weight) and the cargo weight. This information is typically provided by the trailer manufacturer and can usually be found on a placard or label affixed to the trailer.
Determine Tare Weight: The tare weight is the empty weight of the trailer without any cargo. This information can also be found on the manufacturer's placard or label attached to the trailer.
Calculate Payload Capacity: Subtract the tare weight from the GVWR to find out the maximum payload capacity of the trailer. Payload Capacity = GVWR - Tare Weight
Consider Axle Ratings: Each axle on the low bed trailer has its weight rating, which indicates the maximum weight the axle can bear. Make sure that the total weight of the loaded low bed trailer is evenly distributed across all the axles and doesn't exceed any individual axle's weight rating.
Factor in Legal Restrictions: Each region or country has its own regulations regarding the maximum allowable weight for trailers on public roads. Make sure to adhere to these restrictions to avoid penalties or fines.
Account for Tongue Weight: The tongue weight or kingpin weight is the downward force exerted by the trailer's gooseneck onto the towing vehicle's hitch. It's essential to ensure that the tongue weight is within the recommended limits to maintain stability and safety during transportation. The tongue weight typically ranges between 15%-25% of the gross trailer weight, but it's essential to check the specific recommendations from the trailer and towing vehicle manufacturers.
Once all these factors have been considered and the appropriate limits adhered to, you can successfully calculate and optimize the load capacity of a low bed trailer.
Why Required lowbed trailer?
Lowbed trailers play a vital role in the transportation industry for numerous reasons, primarily concerning the hauling of heavy and oversized cargo that traditional trailers or trucks cannot accommodate. Here are some key reasons why lowbed trailers are indispensable:
Heavy Machinery and Equipment: Designed specifically to carry oversized and heavy equipment, such as construction machinery, cranes, excavators, bulldozers, and industrial components, lowbed trailers offer a solution for items that are too large, heavy, or unwieldy for regular trucks.
Oversized Loads: Lowbed trailers are essential for transporting abnormally large cargo, such as massive tanks, turbines, or wind turbine blades. Their lowered deck height allows for cargo to fit within height restrictions and safely pass under bridges or overpasses.
Tall Cargo Accommodation: Lowbed trailers are capable of handling cargo with increased height that cannot be safely or practically transported in standard trailers.
Stability and Safety: Lowbed trailers possess a lower center of gravity in comparison to standard trailers, resulting in enhanced stability during transportation. This stability is vital when carrying heavy and high-value loads over long distances.
Compliance with Bridge and Road Weight Limits: Various countries and regions impose weight restrictions on vehicles traversing their roads and bridges. Lowbed trailers distribute cargo weight more evenly, facilitating heavier transportation without exceeding legal weight limits.
Construction and Infrastructure Projects: Frequently employed in construction and infrastructure projects, lowbed trailers transport heavy construction equipment and materials to remote or challenging worksites.
Energy Sector Applications: Lowbed trailers are commonly used within the energy industry for the transportation of power plant components, oil rig structures, and other large-scale energy project materials.
Mining and Agriculture Transportation: The mining and agriculture sectors rely on lowbed trailers for the hauling of heavy machinery, vehicles, and equipment crucial to their operations.
In summary, lowbed trailers are essential for facilitating the transportation of oversized and heavy cargo across various industries, enabling the safe, efficient, and reliable execution of complex projects and operations.